Hemorrhoids
Hemorrhoids or piles are an uncomfortable burning problem that most people are faced with at least once in their lives. Hemorrhoids are uncomfortable and can be very painful, but they are in most cases not dangerous. Many sufferers do not seek appropriate treatment because they either do not know they have them, are ashamed or fear visiting a physician due to quite uncomfortable and even painful examinations with an anoscope, sigmoidoscope or proctoscope.
Hemorrhoid knots are usually small and a normal anatomical structure in the wall of the rectum. They mostly consist of intertwined blood vessels that differ in structure from typical vessels. A lack of muscles means that vessels have very thin walls and are therefore more susceptible to injury. Beside the blood vessels, hemorrhoids also consist of elastic connective tissue and a layer of smooth muscle tissue. In normal circumstances hemorrhoids participate in the control of liquid excrement (diarrhea) and gas.
 Hemorrhoid related problems arise when frequent gas, liver disease, pregnancy and other factors increase the pressure in the portal vein, leading the blood vessels to swell up. It is a condition similar to varicose veins in the legs. Hemorrhoid related issues are more common in men, but often occur in women during pregnancy and after childbirth. Hemorrhoids are the most common cause of bleeding from the rectum.
Hemorrhoid related problems arise when frequent gas, liver disease, pregnancy and other factors increase the pressure in the portal vein, leading the blood vessels to swell up. It is a condition similar to varicose veins in the legs. Hemorrhoid related issues are more common in men, but often occur in women during pregnancy and after childbirth. Hemorrhoids are the most common cause of bleeding from the rectum.
Enlarged hemorrhoids are caused by a fast and stressful lifestyle. Heredity, population aging, dietary habits and the modern lifestyle are the main reasons for an estimated 50 % of the middle age and elderly population having occasional or frequent issues due to enlarged hemorrhoids.
Types of hemorrhoids
Hemorrhoids are classified in terms of size and position. By position, they are divided into external and internal hemorrhoids, while in terms of size they are divided in four classes.
By position:
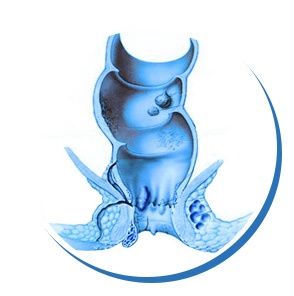
| • Internal hemorrhoids occur in the anus and are less severe due to a smaller number of nerve endings in the rectum. They are normally not painful and can be identified by traces of fresh blood on toilet paper, the toilet bowl or stool. Bleeding is usually small and rarely causes major blood loss. In most cases they consist of smaller engorged veins in the walls of the anus. Hemorrhoids can become larger, hang down and slip through the anus, but can retract on their own or with assistance (gently pushing with a finger). In the worst cases when hemorrhoids do not retract back, they become constricted by the anal muscles, which prevents circulation of blood through the hemorrhoids, creating blood clots and causing great pain. In such cases traces of mucus can be seen on toilet paper or stool.
• External hemorrhoids lie beneath the skin at the outside of the anus. Due to a greater enervation of the anus they are very sensitive and more painful, can itch and sometimes bleed. They are also susceptible to inflammation. These hemorrhoids can become irritated and create blood clots, resulting in very painful thrombosis or lumps.
|
In terms of size, we speak of the following stages:
- First stage: Slightly enlarged hemorrhoids
- Second stage: Considerably enlarged hemorrhoids that do not prolapse through the anus
- Third stage: Enlarged hemorrhoids that prolapse through the anus, but retract on their own or with assistance (gently pushing with a finger) after defecation.
- Fourth stage: Prolapsed hemorrhoids that can no longer be returned into the anus.
|  |
Symptoms
- Itching and discomfort in the anal area
- Burning sensation in the rectum
- Pains in the rectal area
- Painless fresh bleeding during defecation
- Fresh bright red blood present on toilet paper
- Prolapse of hemorrhoids through the anus (felt as bumps on the edge of the anus)
- Pain during or after defecation
- The sensation of the bowel not being completely empty after defecation (leading to more common bowel movements and greater strain)
- Bowel incontinence
The sooner we notice hemorrhoids, the sooner we can begin treatment, leading to better results. The unique HemoSens formula has been proven successful in most cases, consisting of HemoSens capsules and ointment. It can prevent further development of hemorrhoids, limit their symptoms or heal them completely. Success of treatment can be greatly improved by adopting a change of lifestyle, a healthy fibre rich diet, more exercise and drinking more water.
Causes
All activities that increase pressure in the abdomen that lead to expansion and weakening of veins of the rectum can cause enlargement of hemorrhoids. Liver disease is one of the most common causes of hemorrhoids as they increase pressure in the rectal blood vessels. For the most part, these problems are caused by the modern unhealthy lifestyle and improper diet based on processed food, plenty of sugar, salt and alcohol, and mostly affects older people.
Hemorrhoids often occur during pregnancy and after childbirth.
Some of the contributing factors to enlargement of hemorrhoids are:
- Genetic predisposition
- Strain during defecation
- Spasmodic coughing
- Vomiting
- Retaining stools
- Lifting heavy loads
- Chronic constipation
- Chronic diarrhea
- Extensive sitting
- Alcohol
- Lack of physical exercise
- Unhealthy diet and lack of dietary fiber
Prevention
There are many more or less effective methods for treating the symptoms of hemorrhoids, but it should be noted that treatments will be much more successful if certain lifestyle changes are made at the same time.
Such measures are predominantly preventative, but are also recommended for easing the symptoms of hemorrhoids. It is important to maintain soft stools and this is best achieved with a proper fiber rich diet and drinking plenty of water.
- It is important to drink plenty of water: Water aids in thinning the stool. The majority of water is evacuated from the body through urine, but a part is also evacuated through stool. This thins out the stool and consequently reduces strain. An adult person should drink 1.5 to 2 liters of water per day. In order to reduce the symptoms of hemorrhoids it is important to avoid certain drinks such as coffee and alcohol, which have a diuretic effect.
- Eat food rich in dietary fiber: The diet is key in reducing hemorrhoid symptoms. Food rich in fiber aids in creating a balance in the bowels and assures regular bowel movements. The most dietary fiber is found in unprocessed foods, fresh fruit, vegetables and legumes.
- Regular bowel movements: It is important to establish a habit of regular bowel movements. Do not put off bowel movements as waiting hardens the stool and then creates more strain.
- You should also avoid excessive strain during defecation.
- Do not put it off. When you feel the need, do not put it off.
- Avoid tinted or scented tissues.
- Use neutral soap.
- Regular and appropriate exercise helps restore balanced bowel movements.
- During longer periods of sitting stand up and walk around.
Treatment
There are many methods of treatment that can ease symptoms, reduce or even remove hemorrhoid related problems. Success can often be achieved just using measures to soothe symptoms.
Unfortunately, treatment is never permanent and successful mitigation of hemorrhoids does not mean that they will not reappear in the future.
Hemorrhoids can be treated with capsules that have a beneficial effect on the digestion system, reduce pressure on veins in the rectal area, reduce pain and discomfort and shrink hemorrhoids. The ointment is also very popular as it reduces itching, shrinks hemorrhoids, eases pain and discomfort in the area around the anus.
In order to achieve optimal effects, you will need to make some changes in your lifestyle, eat appropriate fiber rich foods, drink plenty of water and do regular exercise.
Measures
There are also certain recommended measures that you can take at home:
- Take warm sitting baths. Pour 10 centimetres of warm/lukewarm water into a wash basin and squat into it for several times a day, especially after defecation.
- Wash the anorectal area using a mild fragrance free soap and water.
- Rinse thoroughly and gently wipe the anus with fragrance free tissues.
Operative procedure
In most cases these measures are effective and completely remedy or soothe hemorrhoid related problems. If problems keep repeating and hemorrhoids become very painful or large scale bleeding occurs, an operation may be necessary. Surgeons utilise the following procedures:
- Hemorrhoidectomy is the classic method of hemorrhoid removal, whereby hemorrhoid knots are excised completely.
- A procedure where veins are identified using ultrasound and then sutured closed to stop the flow of blood.
- Hemorrhoids can also be treated using laser, electrical current or infrared radiation.
- Using an elastic ligature placed around the hemorrhoid. A tied off hemorrhoid then dries and falls off. This technique only allows for the treatment of one hemorrhoid at a time, requiring several procedures over a period of time.